Unlocking the Potential of Color in ESG and Sustainability Reports

Using colors in a sustainability report can significantly impact its effectiveness. Incorporating your company’s brand colors maintains consistency and strengthens your organization’s identity. Additionally, strategic use of bright or contrasting colors can highlight important sections and establish a visual hierarchy, guiding readers through the report.
Colors also evoke emotions, creating a deeper connection with the audience. For example, green symbolizes sustainability, while blue conveys trust. In data visualization, a consistent color scheme helps differentiate data sets in graphs and charts, making the information clearer and easier to understand.
Color is fundamental to the creation of infographics. A well-chosen color palette is essential for creating impactful infographics that effectively communicate information.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15.

The Art of Coloring Sustainability Reports

Highlight Key Information
Color Coding
Environmental Associations
Consistency and Contrast
Maintain a consistent color palette throughout the report for a polished look. Ensure there’s enough contrast between text and background colors to ensure readability.
Explore how a compelling CSR Report can enhance your brand’s impact
👉 Read the full blog on the power of CSR Reports
Cultural Sensitivity
Negative Space
Subtle and Tasteful
Branding Accents
Typography Contrast
Thematic Cohesion
Remember, the goal is to create a visually appealing report that aids comprehension and engagement without overwhelming the reader. Properly leveraging colors can help you achieve this by making your sustainability report both impactful and aesthetically pleasing
Brand Consistency: Start by considering your company’s brand colors. Incorporate these colors into the report’s design to maintain brand consistency. This helps readers immediately identify the report as belonging to your organization.
Color Psychology: Utilize the psychological impact of colors to evoke specific emotions and responses. For example:
- Green: Represents sustainability, growth, and environmental consciousness.
- Blue: Conveys trust, stability, and a commitment to transparency.
- Earth Tones: Reflect a connection to nature and the environment.
- Warm Colors: Can evoke a sense of urgency or passion when used strategically.
However, it is important to use color judiciously and not overuse it. Overuse of color can make the report look cluttered and difficult to read. It is also important to ensure that the colors used are accessible to all readers, including those with color vision deficiencies
Colors play a crucial role in designing a sustainability report that effectively communicates your company’s commitment to responsible business practices. Thoughtful and strategic use of colors can enhance the report’s visual appeal, readability, and ability to engage stakeholders in your sustainability journey.
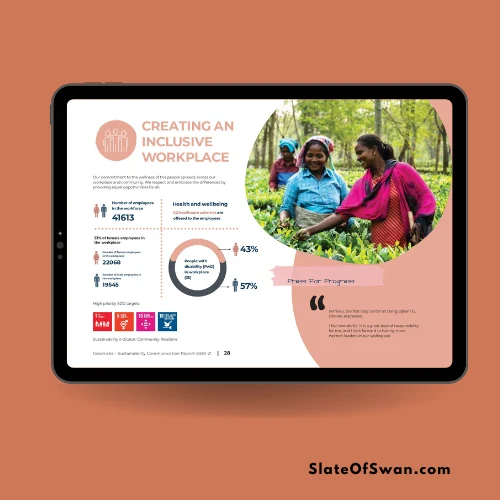
The use of color can play a significant role in designing sustainability and ESG reports. Color can be used to convey information, create visual interest, and enhance the overall readability of the report. For example, using green to represent environmental metrics, blue for social metrics, and purple for governance metrics can help readers quickly identify the different sections of the report 1.
Moreover, color can be used to highlight key data points and trends in the report. For instance, using a bright color like red to highlight a negative trend or a positive trend with green can help readers quickly identify areas that require attention or areas where the company is doing well 1.
Convey the company’s commitment to sustainability. Certain colors are often associated with sustainability, such as green, blue, and white. Using these colors in a sustainability report can help to communicate the company’s commitment to environmental protection and social responsibility.
Make the report more visually appealing and engaging. Well-chosen colors can make a sustainability report more visually appealing and engaging, which can help to keep readers’ attention and encourage them to read the entire report.
Highlight key information. Colors can be used to highlight key information in a sustainability report, such as the company’s environmental goals, its progress towards achieving those goals, and the benefits of its sustainability initiatives.
Differentiate between different sections of the report. Colors can be used to differentiate between different sections of a sustainability report or a CSR report, such as the executive summary, the body of the report, and the appendix. This can help readers to quickly and easily find the information they are looking for.
The company’s branding. The colors used in the report should be consistent with the company’s branding. This will help to create a cohesive and professional look for the report.
The target audience. The colors used in the report should be appropriate for the target audience. For example, a report aimed at investors may use different colors than a report aimed at employees.
The message that the company wants to convey. The colors used in the report should be used to convey the company’s message about sustainability. For example, a company that is committed to reducing its environmental impact may use green as a primary color.
The company’s branding. The colors used in the report should be consistent with the company’s branding. This will help to create a cohesive and professional look for the report.
The target audience. The colors used in the report should be appropriate for the target audience. For example, a report aimed at investors may use different colors than a report aimed at employees.
The message that the company wants to convey. The colors used in the report should be used to convey the company’s message about sustainability. For example, a company that is committed to reducing its environmental impact may use green as a primary color.
Green: Green is often associated with nature and environmental protection, so it is a common color used in sustainability reports. For example, the 2022 Sustainability Report of Microsoft uses green throughout the report to highlight its commitment to sustainability.
Blue: Blue is often associated with water and cleanliness, so it can also be used in sustainability reports to convey a message of environmental protection. For example, the 2023 ESG Report of Unilever uses blue to highlight its water conservation initiatives.
White: White is often associated with purity and simplicity, so it can be used in sustainability reports to create a clean and uncluttered look. For example, the 2022 Sustainability Report of Nike uses white as a background color to make the text and graphics stand out.
Neutral colors: Neutral colors, such as beige, brown, and gray, can also be used in sustainability reports. These colors can be used to create a sense of calm and stability, which can be helpful for conveying complex information. For example, the 2022 Sustainability Report of Coca-Cola uses a neutral color palette to make the report easy to read and understand.

Share this post