Unlocking ESG: A deep dive into ESG materiality assessment
In today’s world, sustainability isn’t just a buzzword. It’s a core part of how businesses operate. Companies are now focusing on their Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) impacts. To navigate this complex landscape, the materiality assessment has become essential. This process helps organizations pinpoint the most critical sustainability issues. It ensures they focus on what truly matters.
This blog post will explore the ins and outs of ESG materiality assessment
What is a materiality assessment?
A materiality assessment is a process that helps companies identify and prioritize the most significant sustainability issues they face. These issues can have a big impact on the company and its stakeholders.
Here’s a simpler way to understand it:
- A materiality assessment looks at the environmental, social, and economic issues that matter most.
- It helps companies focus their efforts and resources on what’s truly important.
- The goal is to create value for the business while also being responsible to the environment and society.
Why is materiality assessment important?
Materiality assessment is more than just a tick-box exercise. It’s a key part of good business strategy. Here’s why it matters:
Focus
It helps companies prioritize the issues that have the biggest impact. This ensures that resources are used effectively.
Transparency
A materiality assessment report shows stakeholders what the company cares about and how it’s performing. This builds trust.
Strategy
The results of a materiality assessment can guide a company’s sustainability strategy and goals.
Risk management
By identifying key risks, companies can better prepare for the future.
Reporting

Materiality assessment in ESG
ESG materiality assessment is a specific type of assessment that focuses on environmental, social, and governance factors.
- Environmental factors include things like climate change, pollution, and resource use.
- Social factors relate to how a company treats people, including employees, customers, and communities.
- Governance factors cover how a company is run, including ethics, transparency, and accountability.
An esg materiality assessment helps companies understand which of these factors are most critical to their business and their stakeholders.

Key terms in materiality
To fully understand materiality assessment, it’s helpful to know some key terms:
Materiality
This refers to the significance of an issue. A material issue is one that can have a substantial impact on a company or its stakeholders.
Stakeholders
These are the groups or individuals that are affected by a company’s activities. They can include employees, customers, investors, communities, and the environment.
Sustainability
This is about meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
ESG
This stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It’s a way of evaluating a company’s impact in these three areas.
The materiality assessment process
There’s no single way to conduct a materiality assessment, but here’s a general outline of the process:
Identify potential issues
The first step is to identify a wide range of sustainability issues that could be relevant to the company.
Gather stakeholder input
It’s crucial to understand what matters most to stakeholders. This can involve surveys, interviews, and workshops.
Assess the significance of issues
The company then evaluates the importance of each issue, considering both its impact on the business and its importance to stakeholders.
Prioritize material issues
Based on the assessment, the company prioritizes the most material issues. These are the issues that will be the focus of their sustainability efforts and reporting.
Document the results
The findings of the materiality assessment are typically documented in a materiality assessment report.
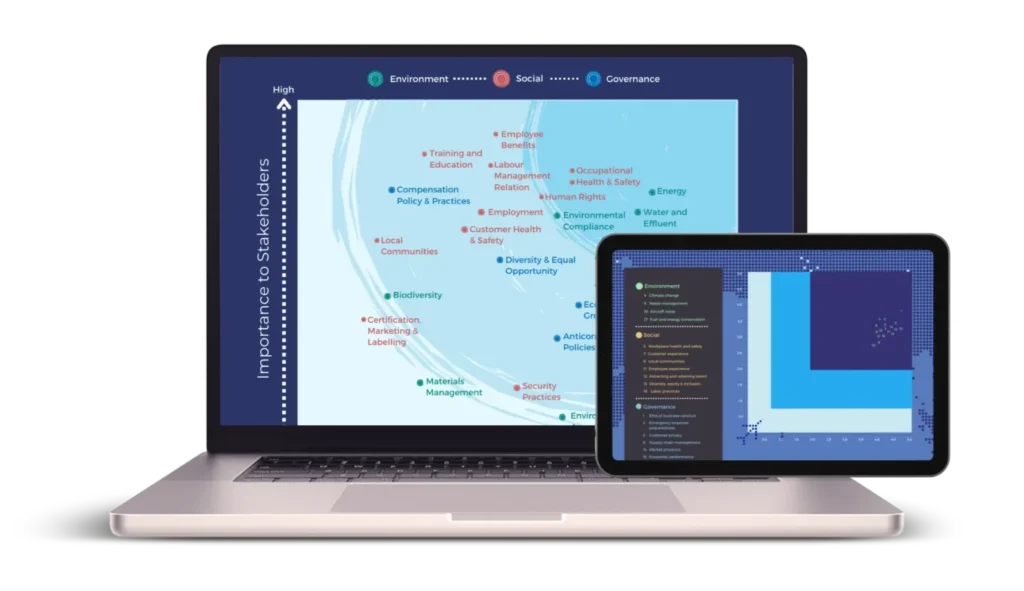
The materiality matrix
A common way to visualize the results of a materiality assessment is with a materiality matrix. This is a chart that plots sustainability issues based on their significance to the company and to stakeholders.
- The x-axis usually represents the importance of the issue to the company.
- The y-axis shows the importance of the issue to stakeholders. Issues that are high on both axes are considered the most material.
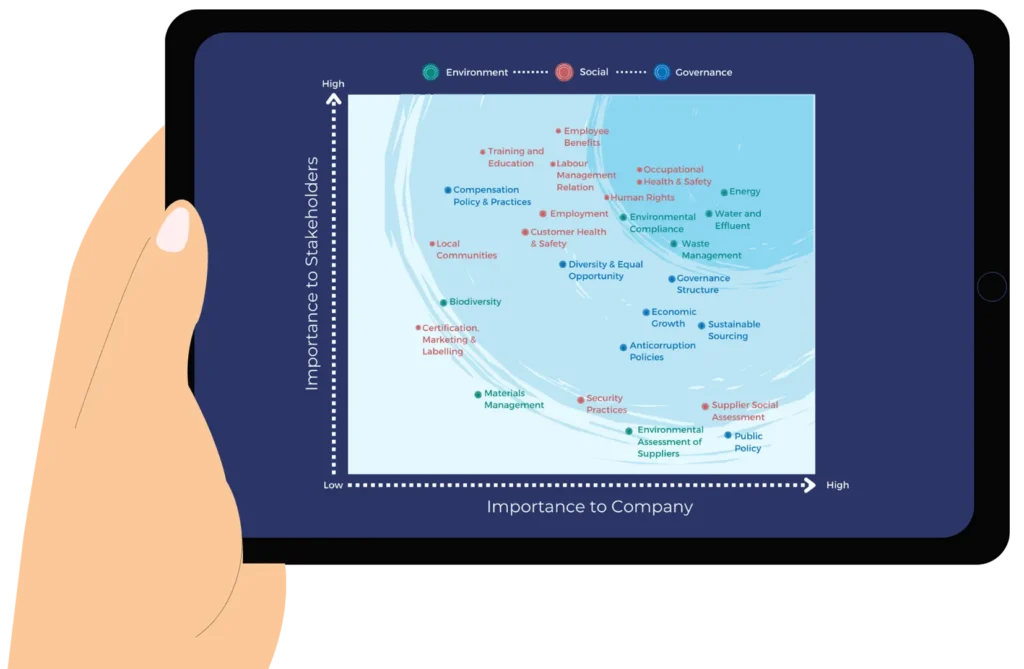
Double materiality assessment
In addition to the traditional materiality assessment, there’s also the concept of double materiality assessment. This approach considers two perspectives:
Impact materiality
Financial materiality
This focuses on how sustainability issues affect the company’s financial performance.
A double materiality assessment report provides a more complete picture of a company’s sustainability profile.
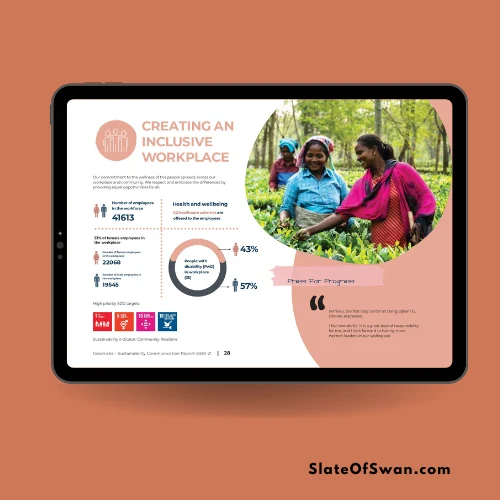
Materiality assessment report
The materiality assessment report is a key document that communicates the findings of the assessment. It typically includes:
- A description of the assessment process.
- A list of the material issues.
- A materiality matrix or other visualization.
- An explanation of how the company will address the material issues.
This report is an important tool for transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Sustainability report design

Creative visualizations of materiality matrices
To make materiality assessment more engaging, companies are using creative visualizations.
Here are some examples:
Heat maps
These use color gradients to show the importance of different issues.
Spider charts
These display data on multiple axes, providing a multi-dimensional view.
Bubble charts
These use circles of different sizes to represent the significance of issues.
Tree maps
These use rectangles to show hierarchical and proportional relationships.
Circular diagrams
These, like pie charts, use segments to show the relative importance of categories.
Flowcharts
These illustrate the relationships and cause-and-effect dynamics between issues.
Icon-based matrices
These use symbols to make the matrix more engaging and easier to understand.
3D matrices
These add a third dimension to provide a more nuanced representation.
These creative designs can greatly enhance a sustainability materiality assessment, making it more accessible and impactful. For your sustainability report design, consider these innovative approaches to effectively communicate your company’s ESG materiality assessment. You can also find inspiration from a sustainability report design agency.

Conclusion
Materiality assessment is a vital tool for companies committed to sustainability. It provides a roadmap for focusing efforts, managing risks, and reporting progress. By understanding what is materiality assessment and how to use it effectively, businesses can create a more sustainable future.
To ensure your sustainability efforts are communicated effectively, consider professional ESG report design. A well-crafted ESG report design can showcase your company’s commitment to ESG and enhance stakeholder engagement. Partnering with an ESG report design agency can help you create a compelling and transparent report.
Remember, the goal is to present complex information clearly and engagingly. This fosters trust and drives positive change. The concept of a materiality matrix in the context of sustainability reports.
Remember, the goal is to present complex information clearly and engagingly. This fosters trust and drives positive change.


Schedule a call
Share this post
news-events